Pigment Ink vs. Dye Ink for Printers
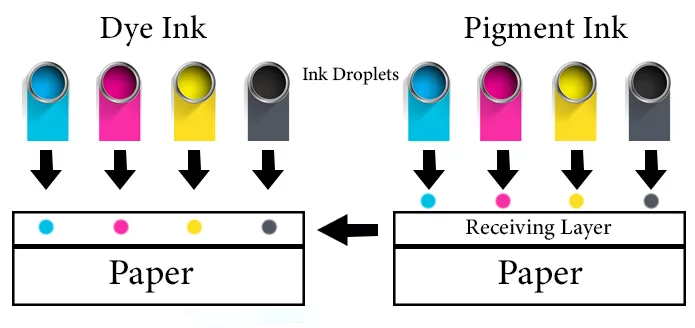
Ink for printers can be broadly classified into two main types: pigment ink and dye ink. Each has its own unique characteristics and is suitable for different printing needs.
Pigment Ink
Pigment ink is made up of solid particles of color that are suspended in a liquid carrier. Here are some of its key features:
Advantages:
- Durability: Pigment inks are highly durable. Once printed, the pigments sit on top of the paper rather than being absorbed into it. This makes the prints resistant to fading, even when exposed to light, heat, and humidity. Prints made with pigment ink can last for decades without significant color degradation.
- Water Resistance: Pigment ink is water-resistant, which means it won’t smudge or run if the printed surface gets wet. This is particularly useful for printing documents or photos that may come into contact with water, such as labels, maps, or outdoor signage.
- Archival Quality: Due to its durability, pigment ink is often considered archival quality. It is a preferred choice for printing important documents, artworks, or photographs that need to be preserved for a long time.
- Less Bleeding: Pigment inks are less likely to bleed through thin papers or cause smudging on multiple pages. This makes them suitable for double-sided printing and printing on thinner paper stocks.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: Pigment inks are generally more expensive than dye inks. This is because the pigments used are more costly to produce and the ink formulations are often more complex.
- Slower Drying Time: Pigment inks tend to have a slower drying time compared to dye inks. This can cause smudging if the printed pages are handled too soon after printing. Some printers may have a drying mechanism or require a longer waiting period to ensure the ink is fully dried.
- Slightly Lower Color Vibrancy: While pigment inks can produce excellent color quality, they may not be as vivid as dye inks. However, advancements in pigment ink technology have significantly improved color vibrancy in recent years.
Dye Ink
Dye ink is made up of water-soluble colorants that are absorbed into the paper. Here are its main characteristics:
Advantages:
- Color Vibrancy: Dye inks are known for their high color vibrancy. They can produce extremely vivid and saturated colors, making prints look more vibrant and eye-catching. This makes them a popular choice for printing photos and graphics where color accuracy and richness are important.
- Faster Drying Time: Dye inks dry quickly, which reduces the risk of smudging and allows for immediate handling of printed pages. This is beneficial for high-volume printing or when time is of the essence.
- Lower Cost: Dye inks are usually less expensive than pigment inks, making them a more cost-effective option for those who print frequently or on a budget.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Durability: Dye inks are less durable than pigment inks. They are more prone to fading when exposed to light, heat, and humidity. Prints made with dye ink may start to fade within a few years, especially if exposed to direct sunlight.
- Not Water-Resistant: Dye inks are not water-resistant and can smudge or run if they come into contact with water. This can be a problem for prints that may be exposed to moisture, such as in a kitchen or bathroom.
- More Likely to Bleed: Dye inks are more likely to bleed through thin papers and can cause smudging on multiple pages. This limits their use for double-sided printing and on thinner paper stocks.
In conclusion, the choice between pigment ink and dye ink depends on your specific printing needs. If you need durability, water resistance, and archival quality, pigment ink is a better choice. On the other hand, if you prioritize color vibrancy, fast drying time, and lower cost, dye ink may be more suitable. Consider factors such as the type of prints you will be making, how long you need them to last, and your budget when making your decision.
